It's troublesome once your Mac starts to run slowly, your MacBook Pro is overheating, or the Mac fan sounds so loud. You may consider it is caused by running too many apps simultaneously or running the Mac computer too long.
However, turning off all the apps or even restarting the Mac changes nothing. The slow computer probably has the kernel_task high CPU usage issue. If you ignore it, your Mac may experience crashes or even won't boot up later.
Here, in this article, we offer you the most efficient solutions to fix the kernel_task high CPU usage problem on your Mac.
How to fix your Mac's kernel_task high CPU usage?
- 1. Cool your Mac
- 2. Quit inessential processes in Activity Monitor
- 3. Reset SMC
- 4. Reset NVRAM
- 5. Reboot Mac in Safe Mode
- 6. Update software
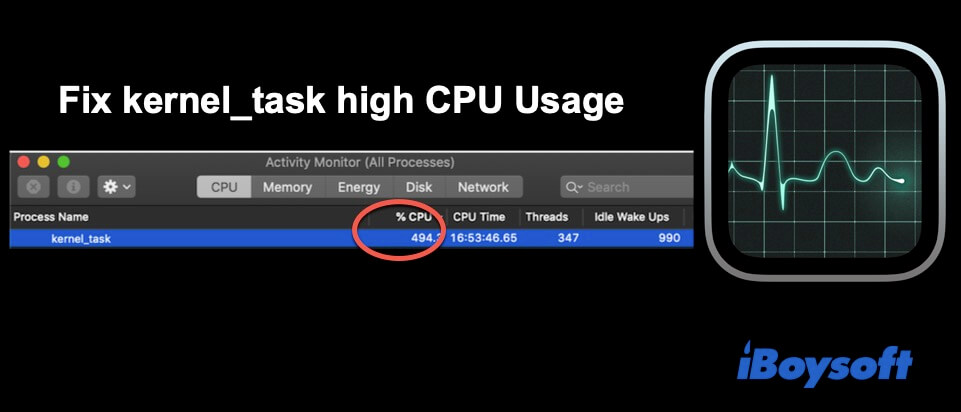
What is kernel_task on a Mac?
Kernel_task is a label in the Activity Monitor utility on a Mac. It represents various activities that proceed flows through the kernel (The kernel is at the core of an operating system).
Whenever you turn on your Mac to play a game, or edit some documents, or so, it will trigger a series of system activities. To consolidate these various activities, the Activity Monitor named them kernel_task.
How to check the kernel_task CPU usage on your Mac
You need to launch Activity Monitor first. Press the Command + Space keys to open Spotlight Search and type "activity monitor" to open it. Or if Spotlight is not working, you can open Finder > Applications > Utilities > Activity Monitor.
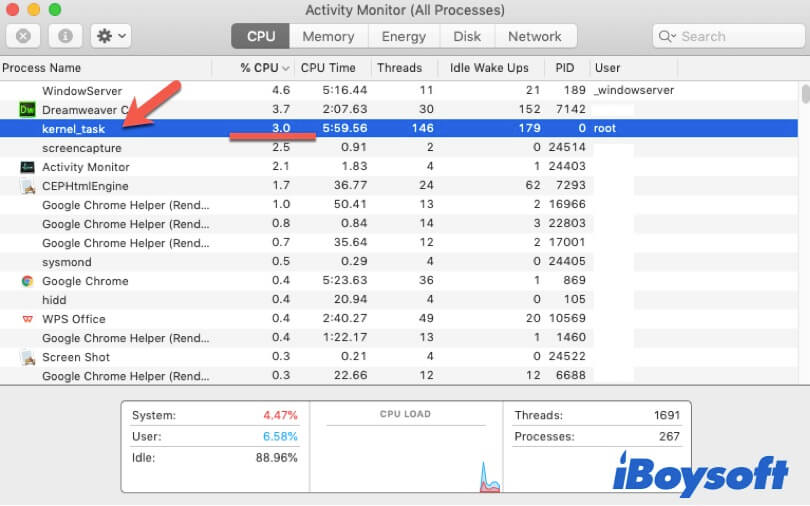
Then, select the CPU tab in the Activity Monitor window and type kernel_task in the box at the upper right corner to locate the kernel_task process.
Usually, kernel_task takes up less than 10% of the CPU. And sometimes, it reaches up to 60%. It's also okay.
But when the kernel_task takes up nearly 100% of your CPU or over and continues from minutes to hours, it indicates that the kernel_task of your Mac takes up high CPU usage. Meanwhile, problems happen, such as your Mac machine running slowly.

What are the causes of kernel_task high CPU usage?
As kernel_task is a label of a series of processes, it's hard to immediately find the culprit that causes your kernel_task with high CPU usage.
After research, we have summarized the common reasons for the kernel_task high CPU usage issue:
- Charge your Mac for a long time.
- Run too many apps at the same time.
- Install a buggy Adobe Flash Player on Mac.
- Enable third-party extensions (or called kext).
- The internal fan of your Mac does not work properly.
- Your Mac is attacked by some malware.
How to fix kernel_task high CPU usage
Unlike other programs that can be force quitted from Activity Monitor, you can't force quit kernel_task on Mac as it stands for a series of activities.
According to the reasons we've analyzed above, you can troubleshoot kernel_task high CPU usage issue through the following solutions and fix the Mac running slow issue.
Cool your Mac computer
Apple has suggested that users should use their Mac devices in acceptable environments with operating temperatures between 50° — 95°F or 10° — 35°C. Otherwise, it will lead to high chassis temperature, and consequently, a high CPU usage to regulate the temperature.
Hence, you can try to disconnect your Mac from charging, unplug the unnecessary peripherals, and move your Mac to a cooling environment. After your computer cools down, check if the CPU usage of kernel_task reduces.
Quit inessential processes in Activity Monitor
Usually, the more programs you run, the more CPU it will take up. Consequently, your Mac slows down. You can open Activity Monitor to quit the inessential processes one by one.
- Search Activity Monitor in the Spotlight Search box on the upper right corner of your screen. Then, double-click to open it.
- Select a process and click the icon at the upper left corner of the Activity Monitor window.
- Click Quit.
- Repeat the above operation on each inessential process.
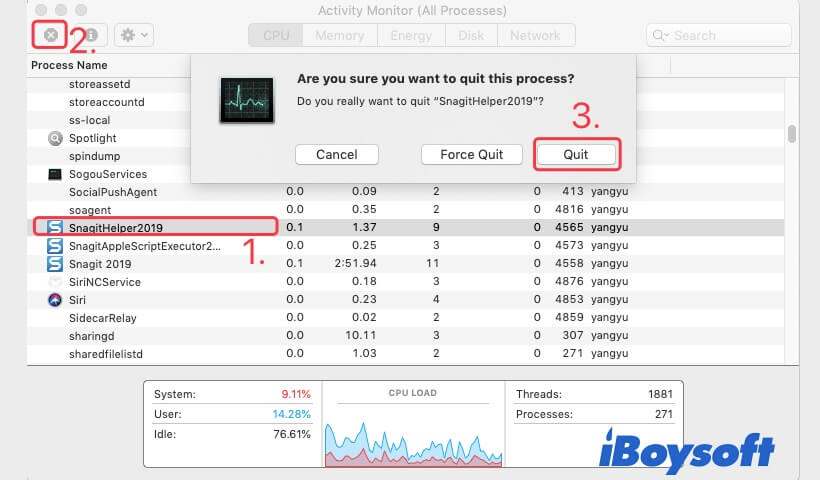
When you quit all the unnecessary apps or programs, shut down your Mac and wait a moment. Then, restart your Mac to check if it gets on the right track.
Reset SMC
SMC (System Management Controller) on your Mac controls power management and hardware like battery, fan, etc. If your fan lasts running at high speed and then brings about the kernel_task high CPU usage issue, resetting SMC may fix it.
Reset SMC on MacBook Pro or MacBook Air:
- Shut down your Mac.
- Press down the Control + Option + Shift (on the right side) keys. Then hold the power button.
Note: For MacBooks without a T2 chip, use the left Shift key instead.
- Release the four keys after ten seconds.
- Turn on your Mac.
Reset SMC on iMac and Mac mini:
- Shut down your Mac and unplug the power cord.
- Wait 10 seconds and then replug the power cord.
- Wait 5 seconds and then press the power button to turn on your computer.
Reset NVRAM
NVRAM (Non-volatile random-access memory) is a small amount of memory that stores OS-related settings to keep your Mac performing properly and boot up quickly.
When kernel_task consumes high CUP and leads to improper Mac performance, resetting NVRAM may fix the trouble.
Here's how to reset NVRAM:
- Turn off your Mac.
- Press down the Option + Command + P + R keys during your Mac reboots.

- Release the keys when hearing the second startup sound from your Mac. If you use a T2-based Mac, release the keys when the Apple logo appears and disappears twice.
If you use an Apple M1 Mac, there's no need to manually reset NVRAM. It will auto-resets if needed every time you start up your Mac.
Boot your Mac into Safe Mode
Some software enables third-party extensions for managing hardware. This has the risk of causing kernel_task with high CPU usage.
So, you can boot your Mac into Safe Mode, which only loads the required extensions and drivers.
To boot an Intel-based Mac in Safe Mode:
- Completely turn off your Mac.
- Hold down the Shift key when restarting your Mac.
- Release the Shift key until you see the login window.
To boot an M1 Mac in Safe Mode:
- Shut down your Mac.
- Hold down the power button until the startup options and the Options icon appear.
- Select your startup disk and then hold down the Shift key and click Continue in Safe Mode.
- Release the Shift key.
If your Mac performs well in Safe Mode, the recently installed third-party software is the culprit. You can remove it from your Mac and restart the computer. Then, your Mac will back to normal.
Update software
It is reported that the kernel_task with a high CPU bug even appears on macOS Big Sur. That's not strange. Commonly, the first version of the new OS always along with some pending bugs.
Or you haven't upgraded your macOS for a long time, resulting in the software not working well with the hardware anymore. Later, problems like kernel_task with high CPU usage pop up. Therefore, proceeding with a software update can fix the bug.
All you need to do is to open System Preferences in the Apple menu. Then, choose Software Update to check if there's any new version released. If there are, update your Mac to the latest version.

Note: Proceeding with Software Update may cause data loss if any errors occur during the update, you'd better back up your important files before updating your Mac.
How to Fix WindowServer High CPU on Your Mac
In this post, you may find 6 ways to fix the WindowServer Mac high CPU problem. In addition, you'll learn what is WindowServer on Mac and Why it eats up so much CPU resources. Read more >>
The kernel_task high CPU usage problem still exists?
If your computer has already updated to the latest OS version, and the above ways fail to fix the kernel_task taking up a high CPU problem, you have to reset your Mac or reinstall macOS to bring your Mac back to the normal state.
FAQs about kernel_task high CPU on Mac
- Q1. How much CPU usage is normal?
-
A
Mostly, kernel_task uses a few to tens of percent of CPU. If the kernel_task takes up to 100% or a few hundred percent of CPU, it is abnormal. At the same time, your Mac runs slowly, freezes, or crashes.
- Q2. Can you stop kernel_task on Mac?
-
A
No. As kernel_task in Activity Monitor is a label that represents a series of activities that proceed since your Mac starts up, you can't quit it or stop it on Mac. You can check in Activity Monitor that the quit button for kernel_task is not available.
- Q3. Why is my Mac CPU so high?
-
A
The reasons for your Mac CPU becomes so high are various, such as your Mac running multiple programs at a time, the outside temperature around your Mac is high, your Mac fan not working well, or your Mac is experiencing malware attack.
- Q4. How to check CPU usage on Mac?
-
A
You should launch Activity Monitor (Under Finder > Application > Utilities). Select the CPU tab in the Activity Monitor window. Then, you'll see the CPU usage of every process.
