Almost all Windows users know this magic combination to open Task Manager: Control + Alt + Delete. When you want to kill unresponsive programs or check Mac CPU usage, this keyboard shortcut is used frequently. But how to open Task Manager on Mac, or what's the Mac Task Manager equivalent? Just keep reading to figure it out.
How to open Task Manager on Mac
Normally, there are four ways to open Task Manager on Mac - Activity Monitor. Three are from the built-in tools: Finder, Dock, and Spotlight, which are convenient but a little cumbersome. Another one is with a useful right-click tool, iBoysoft MagicMenu. Let's view the steps one by one:
Fix 1: Open Mac Task Manager from Finder
- Click Finder in your Dock.
- Locate Applications on the sidebar.
- Select Utilities in the Applications window.
- Double-click on the Activity Monitor icon.
Fix 2: Open Mac Task Manager from Spotlight
- Press Command + Space to open Spotlight.
- Input Activity Monitor in Spotlight.
- As Activity Monitor appears highlighted, hit Enter or click on it.
Fix 3: Open Mac Task Manager from Dock
- Click Lunchpad in the Dock.
- Select Others then open Activity Monitor.
Tips: If you wanna use the Task Manager on Mac frequently, you can open it in the three ways mentioned above, right-click the Activity Monitor in your Dock > Options > Keep in Dock, and you can conveniently see and use it in the Dock.
Fix 4: Open Mac Task Manager from iBoysoft MagicMenu
Maybe the three built-in actions seem a little complicated, but it is highly recommended to use iBoysoft MagicMenu. It is a useful tool designed to enhance your right-click context menu; in other words, you can easily open Mac Task Manager just with a right-click.
- Free download, install, and open iBoysoft MagicMenu.
- Click Quick Access in the left menu and click "+".
- Then you can add the path: Applications > Utilities > Activity Monitor > Open > Import.
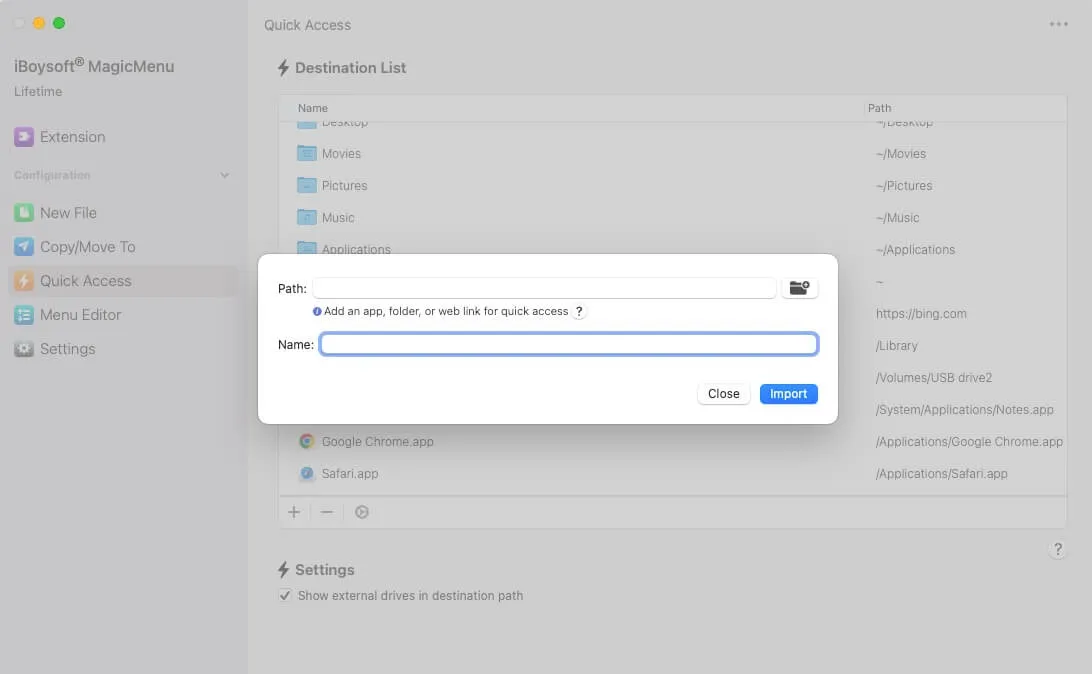
To open Task Manager on Mac, you can just right-click any free space on your desktop, select Quick Access, and choose Activity Monitor.
So easy, right? Share these methods with more people.
What is Task Manager on Mac
Activity Monitor is the Task Manager for Mac, and it functions in a very similar way to how it does in Windows. This macOS utility gives you a general overview of what your MacBook is doing.
This Mac Task Manager monitors Mac activity in real-time, such as processor load, active processes, running applications, and the amount of memory being used. Besides, you can use the Mac Task Manager equivalent to forcibly quit any sluggish programs or non-responsive programs running in the background to free up memory on a Mac or fix your frozen Mac.
How to work with Mac Task Manager
When Activity Monitor is opened successfully, you'll see the window below with 5 apparent tabs.
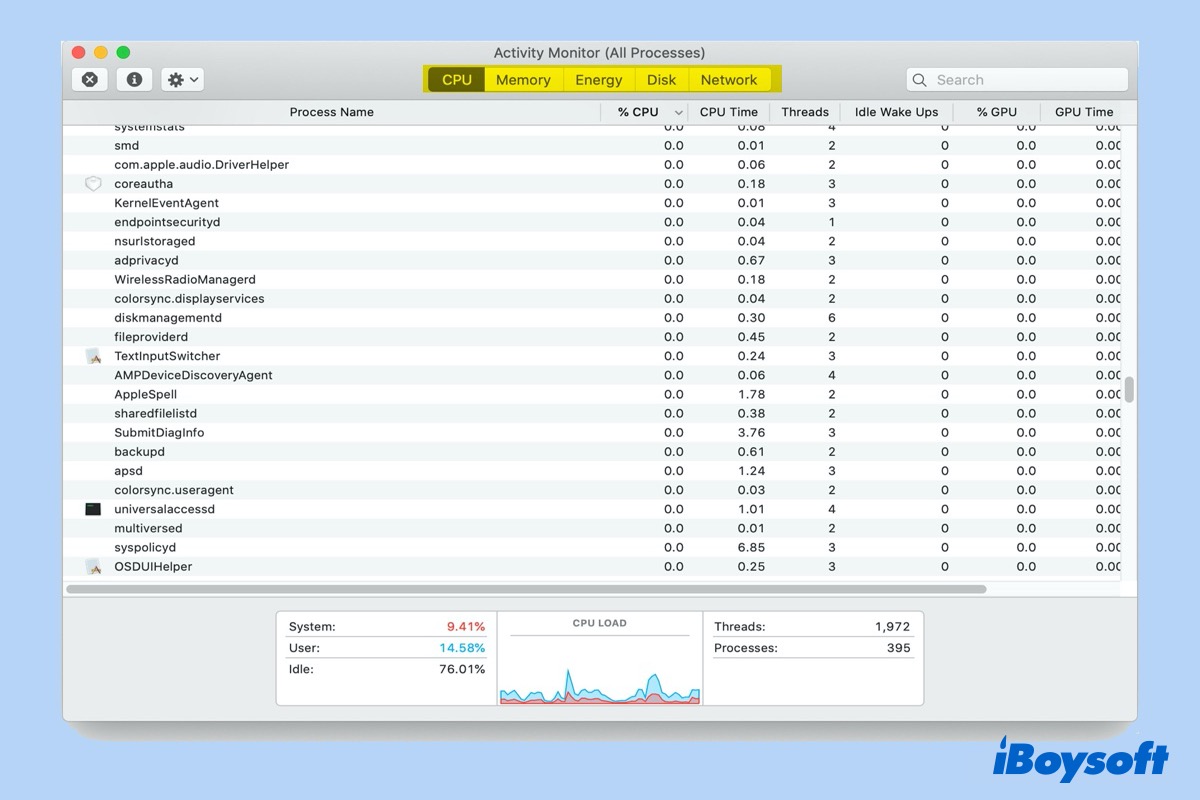
CPU: List all the processes that are currently taking up your Mac's CPU, and demonstrate how long they have been running.
Memory: Reflecting on how much RAM every process is taking up. RAM is directly responsible for the speed of your Mac, so getting rid of heavy users is the fastest way to speed things up.
Energy: Indicating apps and processes that drain your battery, and the energy used by each app or program.
Disk: Showing how various processes interact with your hard drive, rewriting data.
Network: Identifying which processes send and receive the most data.
Knowing the five parts in Mac Task Manager, you can work much better with your MacBook.
Force quit programs via the Mac Task Manager
Using the Activity Monitor to shut the freezing program down is easy. To force quit an app from Mac Task Manager, do the following:
- Open the Activity Monitor on your Mac and click on the app you want to force quit.
- Then click on the X button in the top left corner of the Activity Monitor window.
- Click Quit when you see a pop-up window asking if you want to quit this process.
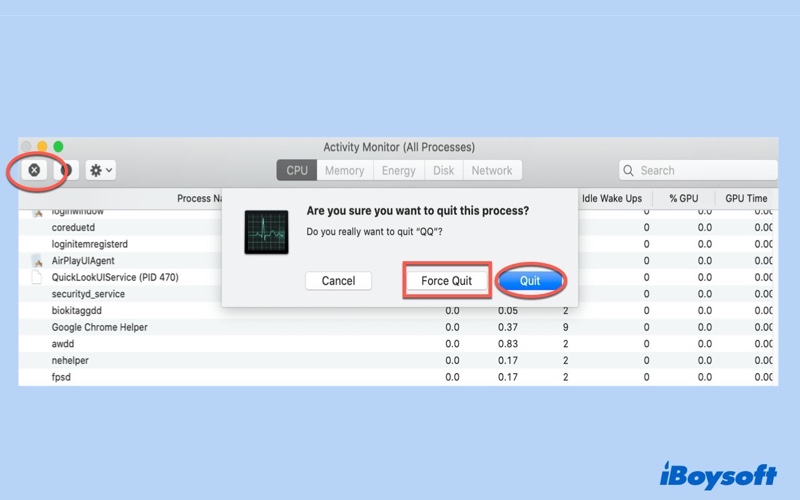
- If the app is still open, choose Force Quit to end the process immediately.
What is the Mac Task Manager keyboard shortcut
Unlike Windows Task Manager, there's no direct shortcut to open the Task Manager on a Mac. And this is the reason why hitting Control + Alt + Delete on a Mac is useless.
Besides using Mac Task Manager - Activity Monitor to force quit programs, another alternative is to click the Apple icon and select Force Quit. You'll learn Mac Task Manager keyboard shortcut for this option is Command + Option + Esc keys.
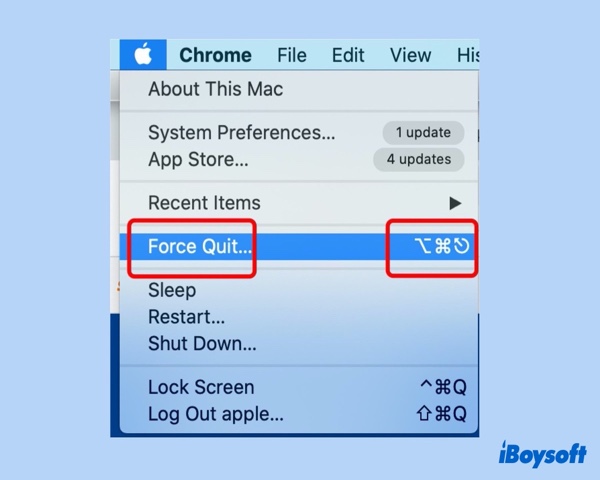
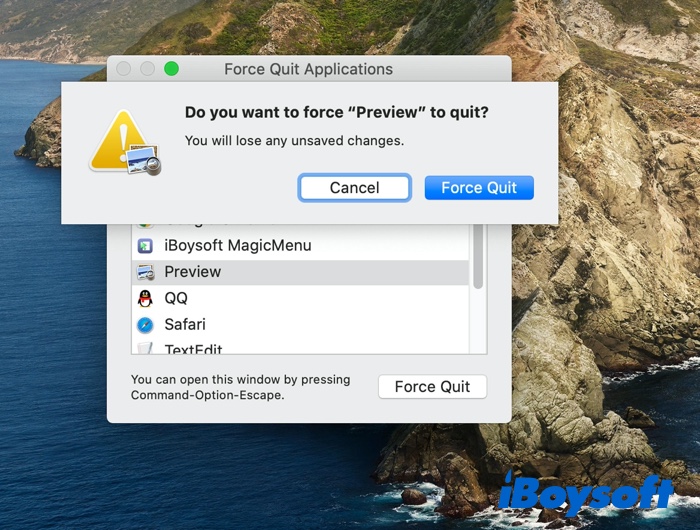
Pressing the Command + Option + Esc shortcut on your Mac, you'll see the following Force Quit utility window. Then just select the non-responsive program and hit Force Quit. When a pop-up appears, choose Force Quit again. Then the selected program shall stop running. And here is a trick: If an application is frozen and not responding, its name will be highlighted in red.
Hope you learn how to open Task Manager on Mac successfully, share this useful post on your social platform.
- QHow to always show Task Manager for Mac in the Dock?
-
A
Open the Activity Monitor from Finder or Spotlight.
Right-click on the Activity Monitor icon in the Dock.
In the menu, choose Options > Keep in Dock.
- QHow do you check the CPU usage via Mac Task Manager?
-
A
Run Activity Monitor from Finder or Spotlight. And in the CPU tab, you'll see the %CPU column. The CPU usage of each process is shown here.
- QAre there better Mac Task Manager alternatives?
-
A
iStat Menus is another Task Manager for Mac that displays graphs for nearly every function of your Mac. This advanced Mac system monitor helps you find out what's wrong or just notice how your Mac behaves in different conditions.
