As the third most widely-used operating system, Linux is an all-available source for all users and devices. Its flexibility, greater security, and high performance have attracted so many professionals and geeks. While due to the trouble of switching from different devices and the cost to own a new one, people prefer to install Linux on their frequently-used Mac.
This article introduces you the brief information about Linux. Also, some recent popular Linux distros are covered in this post. Finally, you can find guidelines on how to use Linux on Mac with specific steps.
Share this post with more people who are interested in macOS and Linux!
A brief introduction to Linux
Following Windows OS and macOS, Linux is the third most popular OS in the world. It enables you to fulfill numerous work that Windows and macOS cannot. Read further to know Linux from a comprehensive perspective.
Free open-source and high customization
Unlike masOS and Windows OS, Linux is totally open-source and available for all people. Everyone can access its significant Kernel source, the core GUN Utilities, and the GUI partition map for free. Due to this, you have high customization that you never find in macOS or Windows. You're even able to change the Linux code to create a unique Linux OS as you like.
Greater security
Note that there is no room for Linux to have malware, for Linux does not give its users admin access by default. Therefore, it limits the damage that users can cause by clicking on links that could be malicious. As a result, the possibility of an operating system crash never happens to you.
Professional usage
As a replacement for Unix, Linux is not a complete operating system for it has no user interface but only a command line. Hence it is pretty suitable for software engineers and application server staff to complete tasks like software designing, unique OS creation, application development, and so on.
If you are not an expert in Linux, don't worry, there also are lots of Linux distros fitting you to run with friendly UI. Don't forget to share this article on your social platform!
Some popular Linux distributions you should know
What you need to bear in mind is that Linux has different versions, or, you can name them as distributions. All of these distributions are built with disparate features to perform diverse work. This part lists some of them below and you can run an eye over them.
Ubuntu: This distribution has a friendly desktop called Unity, which has certain similarities with macOS. Plus, it allows you to change your Ubuntu environment to suit your needs. If you're new hand to Linux, then you'd better start with this distribution.
CentOS: This distro runs faster than other distributions thanks to its lightweight and safe software. The operating system has a longer upgrade cycle of about five years, which means more security and reliability.
Fedora: It offers many graphical tools and useful software for your office work. Meanwhile, it is famous for its endeavor in virus protection, system management, media play, and education. By the way, you can ask for professional help when things go wrong for it is supported by a large community.
Debian: It offers the widest range of software packages than other distributions. Due to its stable software and the longer release cycle, it's regarded as a great distribution for running servers.
Red Hat Enterprise Linux: It is the world's leading enterprise Linux platform used for the development and operation of software and hardware. Also, it is compatible with many third-party software and has a fast security patch cycle.

Linux Mint: It is very similar to Windows OS, and it can support apps like Firefox and LibreOffice. Additionally, you can use an internal software manager to visually search software and install what you need.

All these listed distributions have their advantages and features, and you can experience one or more distributions on your Mac as you like.
Share these wonderful Linux distributions with more people!
How to use Linux on a Mac with a bootable USB drive?
This article takes the Ubuntu distribution for example to show you how to use Linux on a Mac. Your patience is the trump card for the process is a little bit long and tedious.
Before you perform the installation work, here are some significant preparations:
- An empty USB drive with at least 50GB of storage space to make a bootable USB hard drive
- A USB mouse for the Mac mouse cannot be detected by the Linux distro
- A USB keyboard for the Mac keyboard cannot be detected by the Linux distro
Partition your Mac hard drive
If you want to dual-boot Linux and macOS, the partition work of the main internal hard drive is a must.
- Launch the Disk Utility via Home Folder on Mac.
- Click the View button and select the Show All Devices option.
- Select the macOS volumes in the left sidebar to perform the partition work.
- Click the Partition button on the top menu bar, and then the + icon on the lower left corner of the new window.
- Click the Add Partition option in the popup.
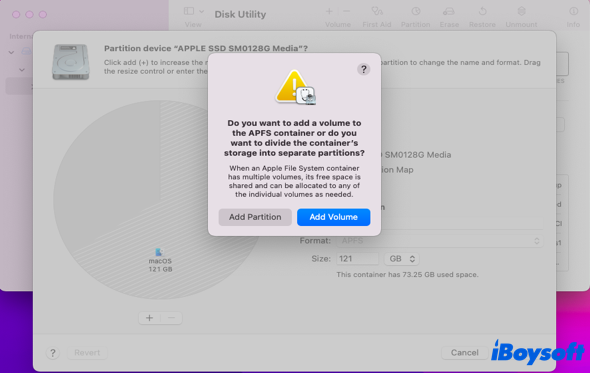
- Name the new partition and then choose the MS-DOS (FAT) in the Format box.
- Determine the partition size and write down it in the Sticky Notes for Mac for later use. You're recommended to set the size at 20GB for Linux OS to place.
- Click the Apply button, and click the Continue option to proceed with the partition work.
Create a bootable USB on your Mac
Be sure the USB drive is totally empty for the following actions will erase everything on it.
- Download the Ubuntu distro to your Mac, which is a DMG file.
- Format the USB drive on Mac to MS-DOS(FAT) and GUID Partition Map in the Disk Utility.
- Download the Etcher app which allows you to burn the Ubuntu distro on the USB flash drive.
- Drag the Etcher app to your Applications folder.
- Run the Etcher app, click the Select Image button, and then select the DMG file that you downloaded.
- Click the Select target button and then select your USB drive.
- Click the Flash option. If you get an error notification, run the Terminal app and type the following command line, then hit Enter.sudo /Applications/balenaEtcher.app/Contents/MacOS/balenaEtcher
- If the error notification still appears that reads your USB drive is unreadable, just click the Ignore button.
When the process ends, you have a bootable USB then.
How to use Linux on a Mac
Since you have a new partition and the bootable USB drive, you can install the Linux distro on your Mac now.
- Power off your Mac and then insert the bootable USB into your Mac.
- Power on your Mac and hold the Option key simultaneously until you see the boot screen with several boot options.
- Control mouse with keyboard to select your bootable USB drive (EFI Boot).

- Select the Install from the GRUB option.
- Follow the on-screen installation wizard, and remember to select Normal Installation.
- Select Something else in the Installation type. This action installs the Ubuntu distro on the partition that you created. If you select other options, it risks installing the Linux distro over the current OS, which will format everything on it.
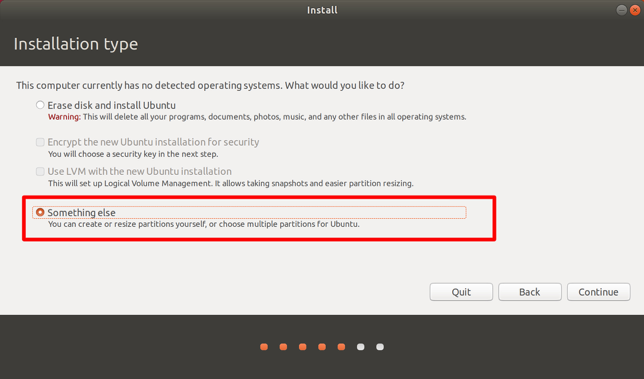
- Select the partition with 20GB space that you have created and then select the Change button.
- Select the Ext4 journaling file system in the Use as box.
- Select the / option in the Mount point box and click OK.
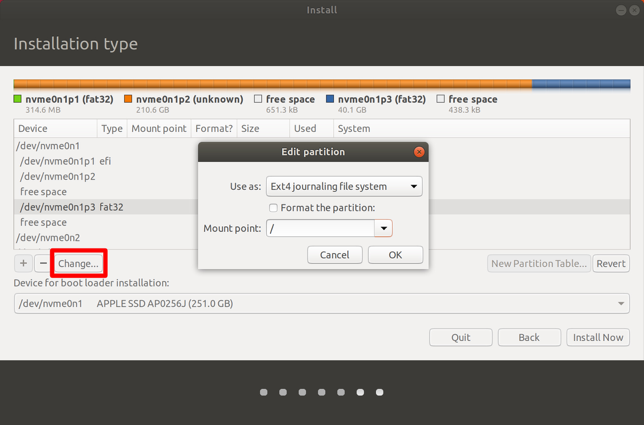
- Click Continue when you're prompted by a popup.
- Click the Install Now button and then click the Continue button when the warning popup prompts.
- Enter your time zone, choose your keyboard layout, and click the Continue option.
- Set up your Linux account. Type in your name, computer name, username, and password.
- Then click the Continue button.
- Wait for the installation process to begin and end.
- Restart the Mac and hold down the Option key simultaneously.
- Choose your Linux OS to start running it on your Mac.
From now on, you can experience all the benefits of Linux OS on your Mac then. You can share your enjoyment and happiness with others by clicking the following share button.
How to use Linux on Mac without a bootable USB drive?
The Linux distros are not single, nor are the methods to install Linux on a Mac. Without a bootable USB drive, you can create a virtual machine to use Linux on your Mac via virtualization apps, such as UTM, Parallels, and Virtual Box. You're recommended to apply UTM for it is completely free and easy to use.
Use Linux on Mac without a bootable USB drive
- Download the UTM virtualization app on your Mac.
- Choose your Linux distribution DMG file and download it to your Downloads file.
- Run the UTM app, and then click the + button to Create a New Virtual Machine.
- Select the DMG file that you downloaded.
- Save your virtualization file and wait for the installation to finish.
A virtual machine allows you to save effort on making a bootable USB drive. Note that some virtualization apps are not free. You can choose the method according to your requirements.
You can also get the answer on how to use Kali Linux on Mac also the installation approaches are almost similar. What you need to do is just make a bootable USB drive for Kali Linux, or, create a virtual machine of Kali Linux, then follow the methods mentioned above to install Kali Linux on your Mac.
Conclusion
Linux operating system definitely works perfectly in certain aspects. This article shows you the basic information about the Linux operating system. Meanwhile, you can have a rough understanding of the most popular Linux distros in this article.
If you're curious about the performance of Linux on a Mac, this post also teaches you how to use Linux on Mac, including with and without a bootable USB drive. However, the installation process is a little bit boring. Just be more patient and then you can use the Linux distro on Mac seamlessly.
Also read:
Share this tutorial with more people!
FAQ about how to use Linux on a Mac
- QIs Linux free for Mac?
-
A
Yes, Linux is an open-source operating system that you can install on your Mac for free. You can make a new partition, create a bootable USB drive, and then install the Linux OS on Mac. Or, you can create a virtual machine via some virtualization app to use Linux on Mac. Then you can experience several advantages of Linux, such as flexibility, privacy, better security, and easy customization on Mac.
- QIs there any other way to experience Linux on a Mac without a bootable USB drive?
-
A
Yes, absolutely there are. You can apply the virtualization apps, such as UTM, Parallels, and Virtual Box to experience Linux on your Mac without the bootable hard drive. Then follow the steps to experience Linux on a Mac: Download the UTM virtualization app on your Mac > Choose your Linux distribution DMG file and download it to your Downloads file > Run the UTM app, and then click the + button to Create a New Virtual Machine > Use Linux on Mac without a bootable USB drive > Select the DMG file that you downloaded > Save your virtualization file and wait for the installation to finish.