You might be shocked to learn that the Windows operating system and the programs running on your computer create temporary files. This article aims to clarify the purpose of temporary files and how they may affect your computer's performance and internal hard drive space.
What are temp/tmp files in Windows
Tmp files, which have the file extension ".TMP," are also referred to as "temporary" or "temp" files. An application or operating system will often create tmp files for backup, storage, or caching purposes.
When memory is required for another activity or to minimize data loss when programs carry out specific tasks, these files are typically created to store information. Apps operate more swiftly as a result of this practice, which helps retrieve information quickly.
Where are temporary files in Windows
Windows normally stores temporary files in two places, but there are other places you can find them as well:
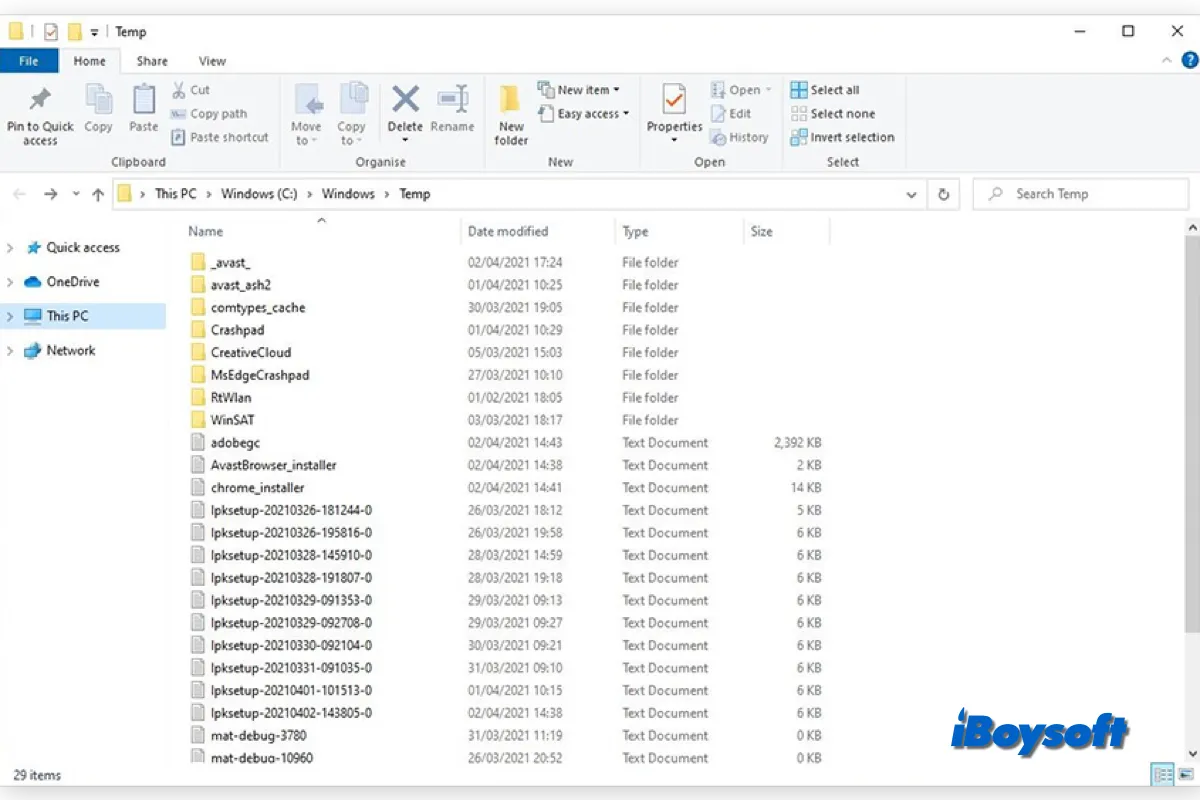
- %systemdrive%\Windows\Temp: The temporary data that the Windows operating system creates. A notice will appear if you click C:\Windows\Temp: "You don't currently have permission to access this folder." To proceed, click Continue. The majority of its contents are .tmp, .temp, and .txt files, as you will see.
- %userprofile%\AppData\Local\Temp: The temporary data created by the User within the user folder when running any software. It is a hidden folder, so before you can see it, you must 'un-hide' System folders under the Folder Options.
A particular software's temporary files may also be found in a sub-folder inside the parent folder of that software. Rarely, a temporary file or folder may be created in the root directory of the C (System) drive.
To access tmp files in Windows:
- Press Windows + R on your keyboard to evoke Windows Search.
- Type %temp% in the box and press Enter to open the temp folder.
Should you delete temp files
Tmp files are produced during operation by different programs and the OS and are meant to serve as temporary placeholders. When they are no longer required, the app that generated the temporary file should likewise automatically remove it from Windows 10.
However, this does not always happen, temporary files build up over time and can take up a sizable amount of storage space. Therefore, regularly deleting temp files in Windows can free up disk space, besides, it also improves the system performance.
How to delete temp files
If you want to delete temp files/folders in Windows to reclaim disk space and speed up your PC once again, there are multiple ways you can choose from:
- Delete temp files from File Explorer
- Remove tmp files using CMD
- Clear Windows temporary files with Disk Cleanup
Way 1: Delete temp files from File Explorer
- Find the temp files from the Start menu, type %temp%, and press Enter.
- Click CTRL + A to select all temp files and press the Delete key.
- If a Folder in Use dialog appears, click Skip to keep removing the chosen temporary files.
- Empty the Recycle Bin to thoroughly remove from Windows.
Way 2: Remove tmp files using CMD
- Click Start or the search box, and type cmd.
- Right-click Command Prompt, and select Run as administrator.
- In the Command Prompt window, you can type the following commands: rd %temp% /s /q or rd “C:\Users\Username\AppData\Local\Temp” /s /q replace "Username" with your account user name.
Way 3: Clear Windows temporary files with Disk Cleanup
- Press the Windows key, type "Disk Cleanup," and click Disk Cleanup to open this built-in tool.
- Under "Files to delete," tick the files or folders you want to delete.
- Click the Clean up system files button to safely clear out the drive space.
- Click OK.

Share to let more people know about tmp files in Windows!