Probably, you are familiar with RAM(random access memory) but unfamiliar with virtual memory in the computer. Both RAM and virtual memory are essential parts to run applications. In this post, we are going to explore every aspect of virtual memory, and you will have a deeper understanding of virtual memory after reading.
What is virtual memory?
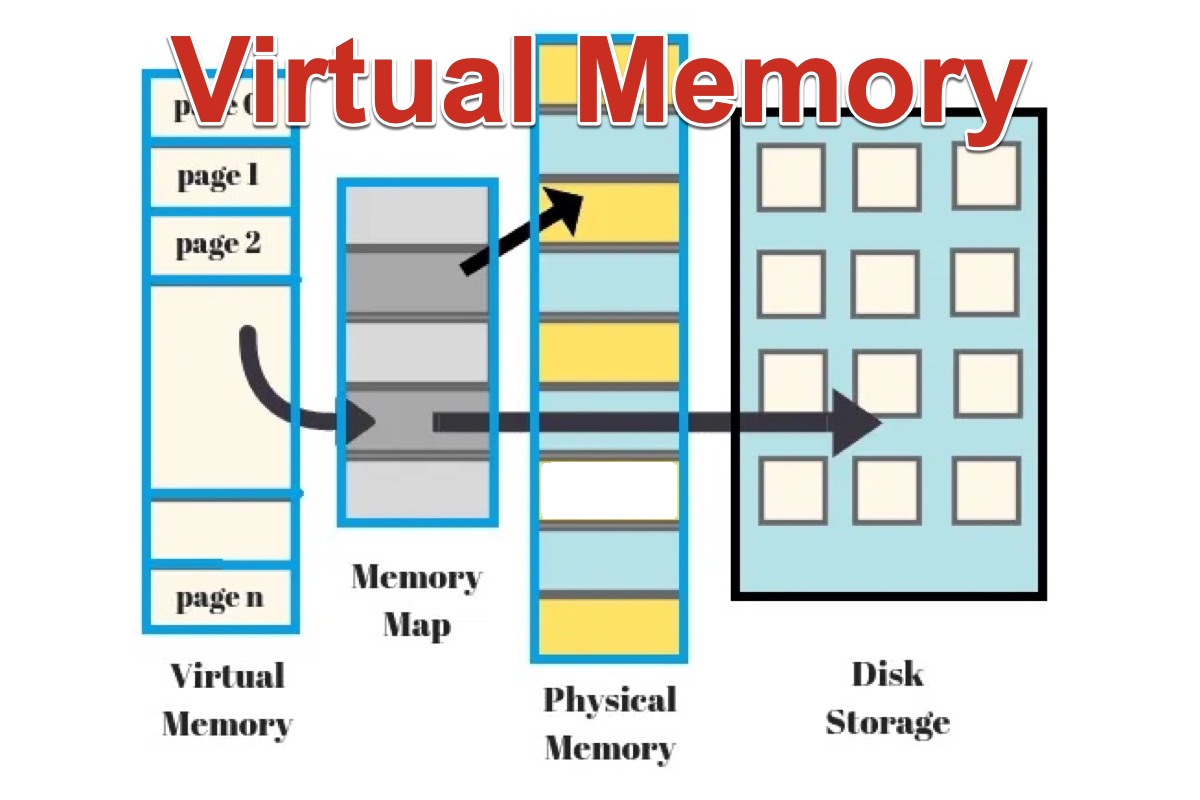
Being different from physical memory or primary memory (so-called RAM), a chip built into the computer's CPU, virtual memory is not a separate component embedded in the motherboard(Virtual memory VS. physical memory). Virtual memory is an area of the computer system's secondary memory storage space, the HDD or SSD installed on your Mac/Windows PC. And virtual memory is used to store the data needed to run applications just like physical memory.
Why virtual memory is necessary?
When you run applications on your computer, RAM stores the data needed to run those applications so that the CPU can quickly access the stored data in RAM to present fluent performance. But if you run memory-consuming applications or launch multiple applications at once, the RAM may be close to being full, given that the capacity of RAM that comes with your computer is limited.
This is where virtual memory comes in. Virtual memory allows users to run more applications than the available physical memory on the system, acting as if it were part of system RAM or primary memory.
How does virtual memory work?
Both hardware and software take part in the process of virtual memory's work. Virtual memory makes the available space on the secondary memory storage to use as RAM when the required memory consumption surpasses the limited RAM. CPU can only read and write data in RAM to work rather than that in virtual memory. So if there is an urgent task but the available RAM is not enough, the memory management unit/memory manager will swap the least used data out of RAM and into virtual memory to release more space on RAM for the current task.
For example, the currently running programs have occupied 4 GB of memory, the total capacity of the RAM, and now you need to perform a new task that needs another 2 GB of memory, then the system will move 2 GB of inactive application's data from RAM to virtual memory to reclaim space on RAM for the current task. And when the data is needed later, the system will copy virtual memory into physical memory for the CPU to access.
Virtual memory pros and cons
Almost all modern computers apply the mechanism to use both physical memory and virtual memory. The obvious advantage of virtual memory is that you can run more applications at the same time. Besides, it allows you to run large programs that the limited RAM can not alone run. In terms of the cost, using virtual memory is less costly than increasing more RAM on your computer, because the virtual memory uses the space allocated from hard disk to store data, and some new computers even don't support increasing RAM capacity.
But the disadvantages are non-negligible. The first is the performance. It takes time to swap files between virtual memory and physical memory, therefore, you can see a distinct decrease in speed when you utilize the virtual memory. Further to say, it could negatively affect the overall performance of the system. And using virtual memory may make your secondary memory storage space nervous if it is not large which may trigger Mac errors such as "Your system has run out of application memory" and "Your disk is almost full".
FAQs about virtual memory
- QIs virtual memory the same as RAM?
-
A
RAM is physical memory that holds the applications, documents, and procedures on a computer. Virtual memory is logical memory and is a storage area that stores the files on your hard drive for retrieval when a computer runs out of RAM.
- QWhat are the types of virtual memory?
-
A
There are two types of virtual memory, namely paging and segmentation. Paging divides memory into small blocks nearly about 4 KB in size, and the segmentation divides memory into segments of varying lengths.
- QHow to check virtual memory usage on Mac?
-
A
You can check virtual memory usage on Mac in the macOS tool - Terminal. Launch the Terminal and choose the Memory tab, then you will see the chart and table at the bottom. You will see an indicator named 'Swap Used', that indicates how much virtual memory has been used on Mac.
- QHow large could the virtual memory be?
-
A
Theoretically, virtual memory can use all the available space on your hard drive to store application data. Max limitation is physical disk space. But it is recommended that users do not increase virtual memory beyond 1.5 times the amount of physical RAM present. So a system with 4 GB RAM should have virtual memory of no more than 6 GB.