Nowadays, many users are familiar with modern SSDs and high-speed SATA SSD drives. Some old technologies like the Parallel ATA hard drives, are also important, especially when dealing with legacy systems or recovering old data.
So, what exactly is a PATA hard drive, and how does it compare to newer storage interfaces?
How PATA Works and PATA Use
PATA stands for Parallel Advanced Technology Attachment, a type of interface standard used to connect hard drives and optical drives to a computer's motherboard.
PATA works by transferring data in parallel across multiple wires using a flat ribbon cable, usually with 40 or 80 conductors. It supports up to two devices per cable, configured as either a master or a slave. Data transfer rates typically range from 33 MB/s to 133 MB/s, depending on the version.
PATA drives were widely used in desktop computers, laptops, and servers for decades. Today, they're mostly found in older machines, legacy industrial equipment, or used for data recovery from obsolete systems.
Advantages and disadvantages of PATA
Like any technology, Parallel ATA drives have both benefits and drawbacks. You can see the table below:
| Pros | Cons |
| Compatible with many older systems and motherboards | Much slower than modern SATA or SSD storage options |
| Inexpensive for legacy system repairs or upgrades | Ribbon cables are large, restricting airflow inside cases |
| Reliable for decades of use before newer interfaces emerged | Only two devices per cable, with master/slave setup often requiring manual configuration |
Hope this summary can help you, and please share our post.
How to know if the drive is PATA on Mac/Windows
If you're unsure whether a hard drive is PATA, here is how to check it on Mac or Windows.
On Windows
- Right-click on the Start menu and select "Device Manager".
- Expand the "Disk drives" section.
- Right-click on a listed drive and select "Properties".
- Under the Details tab, choose Hardware Ids or Bus Type. A PATA drive may show as IDE.
Alternatively, you can open System Information and look under Components > Storage > Drives for connection type details.
On Mac
- Apple Menu > About This Mac > More Info.
- Scroll down and click "System Report".
- Under Hardware > ATA or Storage, you can view detailed information about the connected drives.
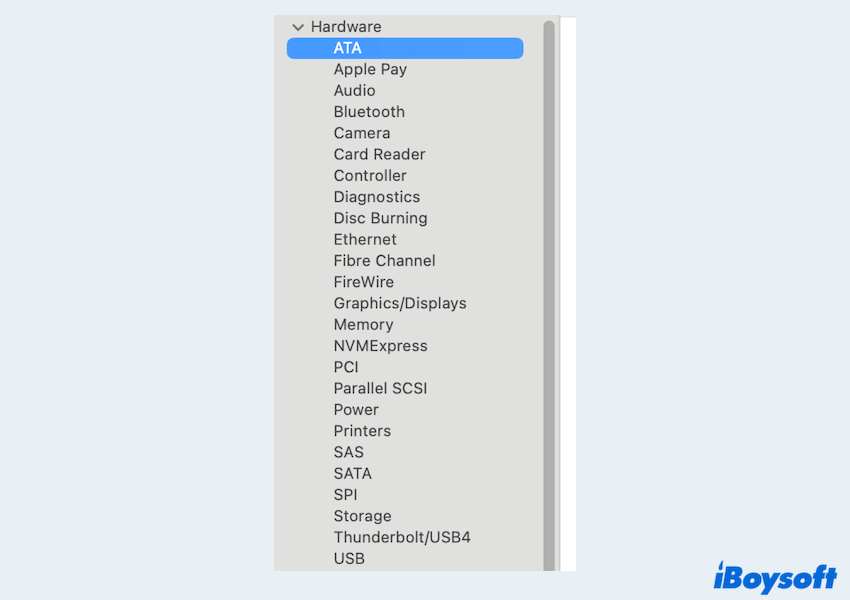
- A PATA drive will usually appear under the ATA section and will not list SATA or NVMe as the connection type.
Is PATA better than SATA?
PATA and SATA are both storage interfaces, but they differ significantly in design and performance.
| Feature | PATA | SATA |
| Data transfer | Parallel | Serial |
| Max speed | Up to 133 MB/s | Up to 6 GB/s |
| Cable type | 40/80-wire ribbon cable | Narrow 7-pin cable |
| Devices per cable | 2 | 1 |
| Hot-swapping | Not supported | Supported |
| Common use | Legacy systems | Modern desktops |
SATA replaced PATA in the mid-2000s due to its faster speeds, simpler cable design, and better system airflow. Today, SATA is still widely used, though being gradually replaced by NVMe and SSD technologies.
Conclusion
A PATA hard drive is an older type of hard disk that uses a parallel interface for data transfer. While it's no longer used in modern computers, it remains important for legacy system support and data recovery.
If you're managing older devices or need to recover data from a vintage system, recognizing a PATA hard drive and its limitations is a helpful skill in your tech toolkit. Share this post.
