Partition schemes manage how data is stored on a disk. You see GUID Partition Map when erasing a hard drive in Disk Utility on your Mac. It catches your eye when you learn what the GUID Partition Map is and the differences between it and the other two schemes on the list - Master Boot Record and Apple Partition Map.
Well, we'll answer all your questions about the GUID Partition Map. You'll learn GUID Partition Map and its main uses, GUID Partition Map vs. Master Boot Record vs. Apple Partition Map, and how to format a drive to GUID Partition Map on Mac.
What is the GUID Partition Map?
GUID Partition Map is a partition scheme that organizes partition tables on physical storage devices like HDDs and SSDs with globally unique identifiers (GUIDs). It makes hard drives with over 2 TB have a robust structure so that they can contain a large number of partitions stably and securely.
It is the primary partition option for hard drives on all modern Mac computers and is also often used on newer Microsoft Windows-based PCs. Different from the name in macOS, GUID Partition Map is known as GUID Partition Table (GPT) in Windows which was introduced as part of the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) standard.
Go to help more people learn what the GUID Partition Map is.
Can Windows read GUID Partition Map?
Yes, Windows supports and reads hard disks formatted with GUID Partition Map. GUID Partition Map is named GUID Partition Table in Windows. Microsoft enabled full support for GPT since Windows Vista.
However, the GUID Partition Table requires a UEFI-based system rather than the older BIOS-based systems in Windows. A Windows computer can boot from GPT-formatted disks only on UEFI-based systems.
GUID Partition Map vs. Master Boot Record
GUID Partition Map (or GPT) is a successor of Master Boot Record (MBR). Both of them support Windows and macOS, but GPT vs. MBR have different limitations on the number of supported partitions, disk size, protection on partition table and data integrity, boot, etc.
| GUID Partition Map (GPT) | Master Boot Record (MBR) | |
| Standardization | Part of the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) standard. | Located in the first sector of a storage device. |
| Number of supported partitions | Support up to 128 partitions on Windows and macOS. | Up to four primary partitions. When creating more partitions, one of the primary partitions can be an extended partition that can contain additional logical partitions. |
| Supported disk size | Over 2TB with a theoretical limit of 9.4 ZB. | Up to 2TB in size. |
| Partition table and data integrity protection | Store multiple copies of the partition table across the disk for redundancy. | No |
| Supported boot | Boot UEFI-based systems (some UEFI systems can also boot from MBR disks). | Boot older BIOS-based systems. |
| Compatibility | Often used on modern macOS but also supports most modern Windows versions and Linux. | Frequently used on older Windows versions and also compatible with macOS and firmware. |
GUID Partition Map vs. Apple Partition Map
GUID Partition Map (GPT) is the modern partition scheme that supports both macOS and Windows while Apple Partition Map (AMP) is only for macOS.
The two partition schemes are both part of the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) standard but have a lot of differences in other aspects.
Here's the table of GUID vs. Apple Partition Map:
| GUID Partition Map (GPT) | Apple Partition Map (AMP) | |
| Supported disk size | Over 2 TB and up to 9.4 zettabytes. | Up to 2 TB. |
| Number of supported partitions | Up to 128 partitions by default on macOS and Windows. | Up to 32 partitions. |
| Partition table and data integrity protection | Store multiple copies of the partition table across the disk for redundancy. | No |
| Compatible operating systems and devices | Modern macOS, especially on Intel-based and newer Macs. | Older macOS and Apple hardware. |
| Usage | Both boot drives and data drives. Default partition scheme for modern macOS and Windows. | Older Mac OS versions and Mac devices. |
How to format a drive with GUID on Mac?
On a Mac, you need to use Disk Utility to help you format a hard drive with GUID Partition Map.
- Go to Launchpad > Other > Disk Utility.
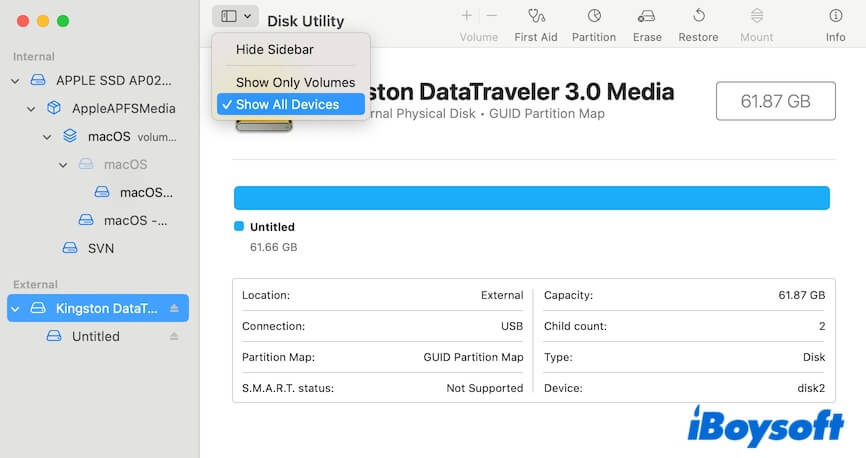
- Click View on the toolbar and choose Show All Devices to show the whole external drives on your Disk Utility sidebar.
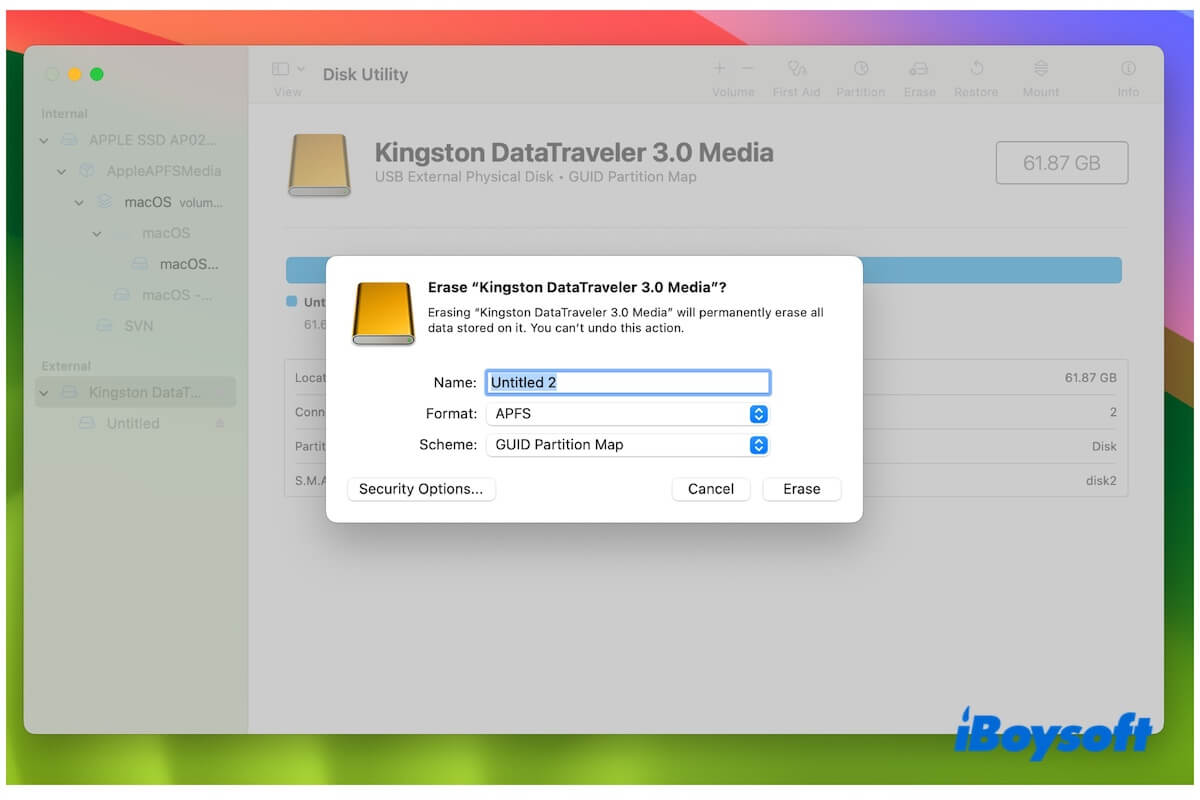
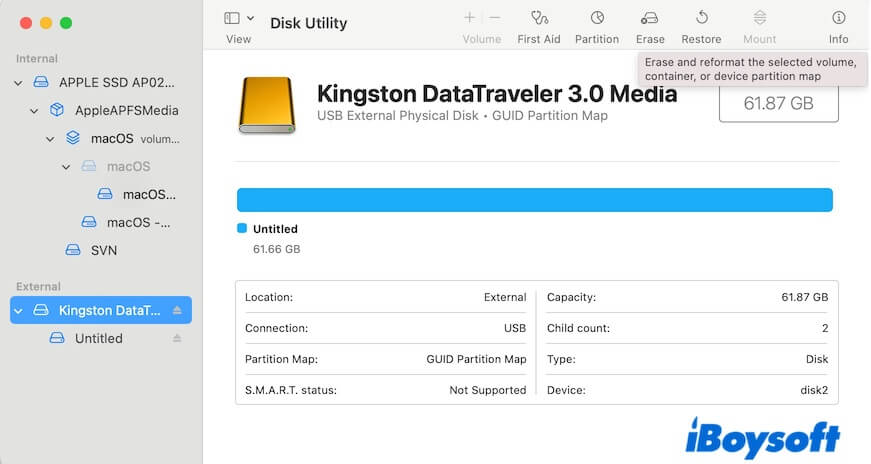
- Select your external hard drive on the sidebar and click Erase.
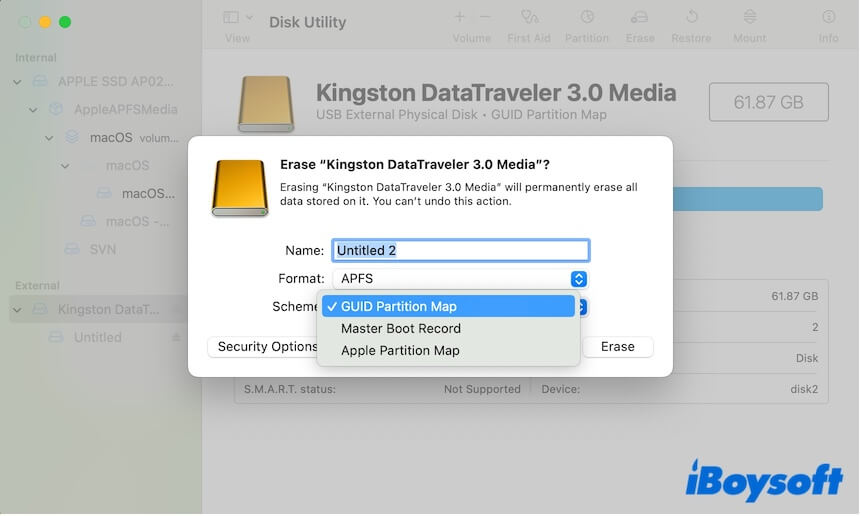
- Enter a name, choose a format, and select GUID Partition Map as the scheme.
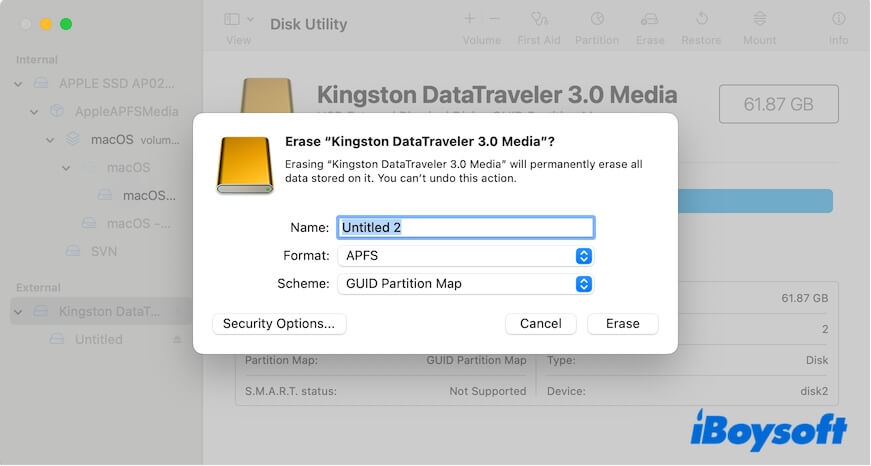
- Click Erase and wait for the process to end.
If you format an external hard drive or USB drive on an older Mac running with an older macOS version, you'll find the GUID Partition Map not showing on the formatting window. Also, if you format a volume on your Mac, there's no option for partition scheme selection.
If this post helps you get a full learning of GUID Partition Map, share it with others.