When you format a drive or a disk, you can see two options: quick format and full format. The choices may seem similar at first glance, but they serve different purposes and have distinct impacts on your storage device.
Knowing the differences of quick format vs full format can help you make the best decisions for your needs, whether it's for data security, speed, or preparing your drive for a specific use. Moreover, you can learn how to format on your PC.
Differences between quick format and full format
What is quick format and what is full format? What are the differences between quick format and full format?
A quick format is a rapid process without inspecting the drive for damaged sectors. It effectively removes file references, making the storage device appear empty. However, the data still exists physically on the drive, and it can be recovered by reconstructing the volume's structure.
In contrast, a full format completely deletes all files on the drive, updates or preserves the file system, and scans for damaged sectors. This method takes significantly longer than a quick format.
Both quick and full formats are supported for FAT(FAT32 and exFAT) and NTFS file systems in Windows. Now you can see the main differences between them:
| Features | Quick Format | Full Format |
| Erase data | No | Yes |
| Recover data | Possible | Impossible |
| Speed | Faster | Slower |
| Check bad sectors | No | Yes |
| Scan errors | No | Yes |
After knowing the table of quick format vs full format, let's see the advantages and disadvantages of quick format and full format. Why not share these differences?
Pros and Cons of quick format and full format
Here, we will discuss the pros and cons of quick format and full format in detail, keep reading.
Quick format's pros and cons:
| Pros | Cons |
| High speed | Can't resolve any problems |
| Can delete viruses | Insecure erasing method |
| Can recover data after formatting | Can't detect bad sectors |
Full format's pros and cons:
| Pros | Cons |
| Can solve drive's issues | Time-consuming |
| Through data erasure | Put additional wear on the drive |
It's important to understand that any formatting tool can potentially lose your data, files, or system. Therefore, you should be well-prepared before you start the formatting process. So make sure to back up your files before formatting.
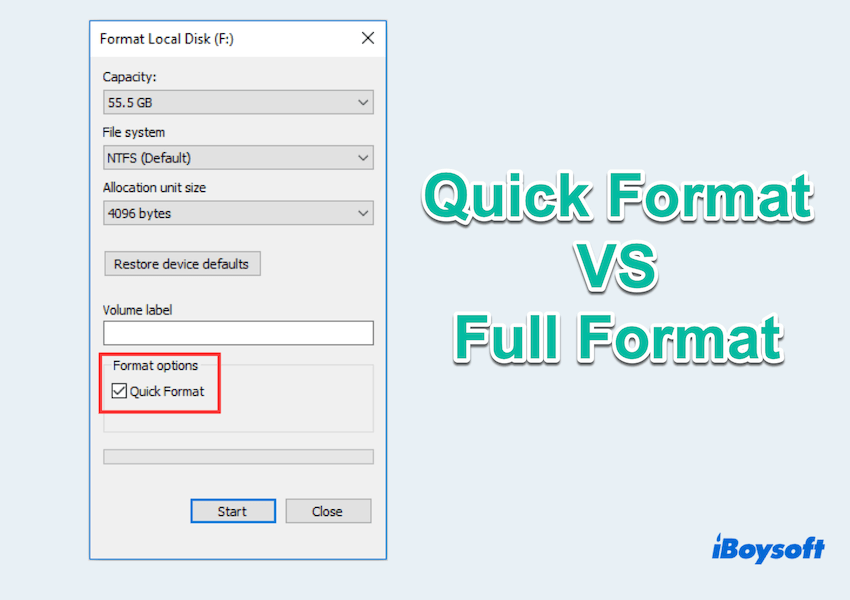
Now you must have a question: Should I choose quick format or full format? After knowing the bad and good parts, see the cases.
- Quick format: Quick clearing a drive for immediate use, setting up a new drive, the drive needs to be ready for use as soon as possible and data security is not a major concern...
- Full format: Prepare a drive for sale or transfer, dealing with older drives, data security, and integrity are critical...
Now you can make a decision for quick format vs full format for certain situations, and share this post with more people.
Bonus: How to format drive on Window
Formatting a drive is easy both on Windows, please follow:
Quick Formatting/Full Formatting a drive on Windows
- Press Windows and X and select Disk Management.
- Right-click the drive you want to format and choose Format.
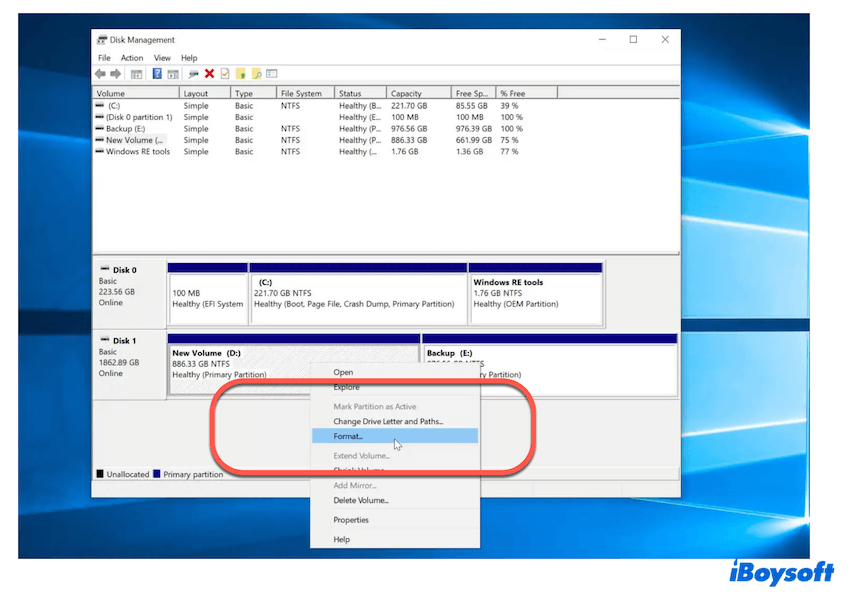
- Select the file system and choose whether to perform a Quick Format or uncheck it for a Full Format.
- Click OK to start the formatting process.
Or you can know other ways to format a drive on Windows. If you choose the quick format, and you want to recover data from it, you can download the effective tool iBoysoft Data Recovery to recover them~
Conclusion
Choosing between Quick Format vs Full Format depends largely on your specific needs and circumstances.
For rapid preparation of a disk with minimal data security requirements, a quick format is often the best choice. However, when security and thoroughness are paramount, or when dealing with older disks, a full format provides the depth and reliability needed.
Understanding these differences ensures you can make the most informed decision for your storage management tasks.
