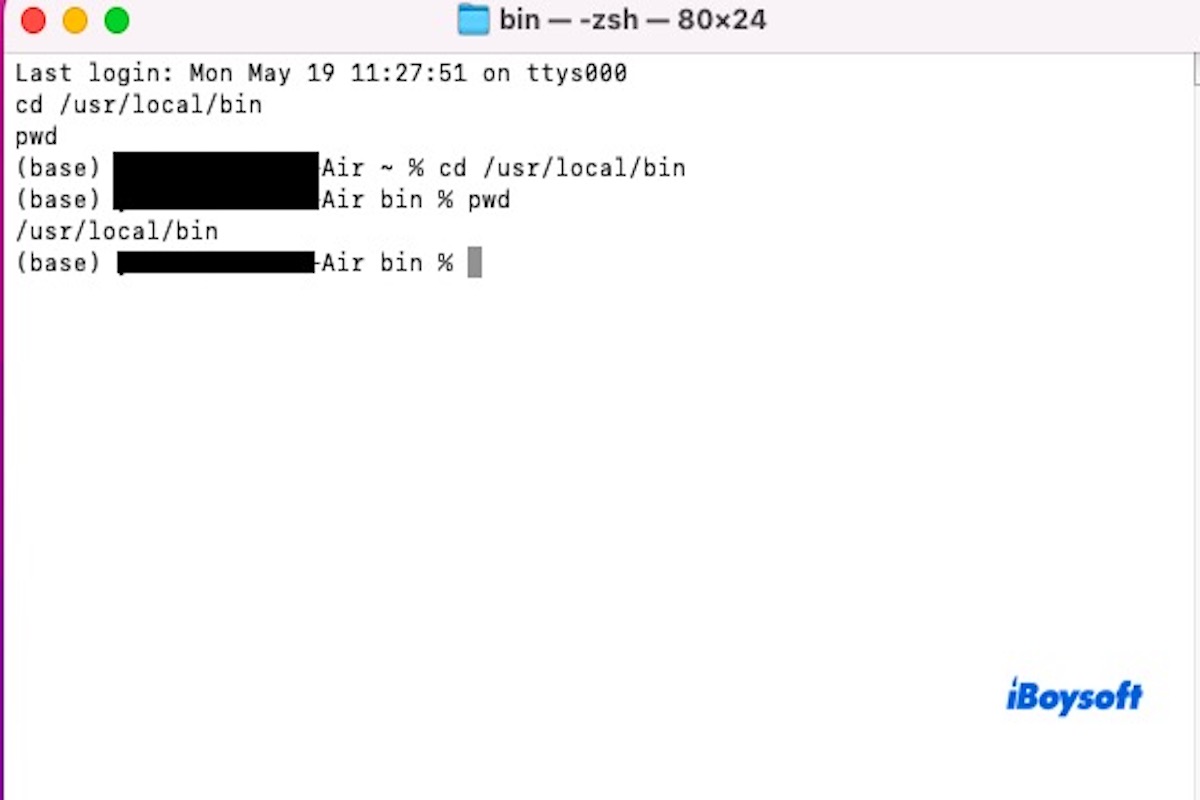
Whether you're navigating your file system on Linux or macOS, understanding your current location in the Terminal is essential. That's where the pwd command comes in.
In this article, we'll explain what the pwd command does and how to use it effectively on both Linux and Mac systems.
What is the Linux pwd command?
The pwd command is commonly used in the Terminal of Linux and macOS. It stands for “print working directory”, which means to display the current working directory. When you type pwd and press Enter, the system will show the full path of the directory you're currently in.
This command is handy when performing file operations, particularly after navigating through multiple directories. It helps you confirm your current location at any time, reducing the risk of making mistakes.
Under the hood, pwd reads the environment information of the current shell session and returns the absolute path of your working directory. No matter how many times you've changed directories using the cd command, pwd will accurately display your current location. It doesn't modify anything on your system — it's simply a tool for displaying your path.
Share this part with more people if you find it useful!
What are the examples of the pwd command?
The most basic use of the pwd command is to check your current directory. When you first open the Terminal or after navigating through multiple directories using the cd command, typing pwd will display the full path of your current working directory. This helps ensure you're operating on the correct files in the right location.
If you want to copy a file to your current directory, you can use $(pwd) to dynamically get the current path. This is especially useful in scripts or complex commands that require path references.
cp ~/Documents/file.txt $(pwd)
In automation scripts, pwd can be used to print the script's current running directory, which helps debug or generate logs that include path information.
#! /bin/bash
echo "This script is running from: $(pwd)"
Additionally, if you're doing remote system administration, you can use this command after logging into a remote server to quickly check your default login directory:
ssh user@remote-server 'pwd'
What is the difference between ls and pwd?
The pwd and ls commands are two of the most commonly used Terminal commands in Unix-like systems such as Linux and macOS. Both are read-only commands, which means they don't modify any files or directories but simply display useful information. While they are both related to directory operations, their purposes and functions are quite different.
When you type pwd in the Terminal and press Enter, the system displays the full path of your current working directory. This command is especially helpful when you've navigated through multiple directories and want to confirm your current location within the file system.
In contrast, ls, short for “list,” is used to display all files and subdirectories within the current directory, or within a specified directory path. It's mainly used to check what items are inside a folder, including files, subfolders, and, optionally, hidden items.
In simple terms, pwd tells you “which directory you're in,” while ls shows you “what's inside that directory.” By using these two commands together, you can easily understand both your current position in the file system and the contents of any given folder.
Share this article with more people to let them learn the difference between ls and pwd!