Image file formats play a crucial role in digital image storage, encoding, and display. Each file format has its unique advantages, limitations, and use cases.
This article will explore different image file formats, explain their characteristics, and provide some common examples. Furthermore, you will also learn how to change the image file format.
What are image file formats?
Image file formats are the way digital images are stored, determining how the image is saved, compressed, and displayed. Each format has its characteristics and is suitable for different purposes. For example, some formats are ideal for storing high-quality photos, while others are better for simple graphics or animations.
Image file formats are mainly divided into two types:
Raster formats: These are pixel-based formats, such as JPEG, PNG, and GIF. Each pixel contains color information, and the resolution (number of pixels) determines the quality of the image.
Vector formats: These use mathematical formulas to define shapes, lines, and colors, allowing for lossless scaling and maintaining clarity. SVG is one of the common vector image formats.
Share the information about image file formats with more people!
What are the most common image file formats?
The most common image file formats are widely used for various purposes, such as photography, web graphics, design, and printing. Here's an overview of the most frequently encountered formats:
JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group)
JPEG is one of the most commonly used image formats in our daily lives, especially for storing photos. It uses lossy compression, which significantly reduces the file size by discarding some image details, making it ideal for web use and social media, particularly when fast loading times are necessary. Although compression slightly reduces image quality, the difference is often not noticeable to the naked eye.
PNG (Portable Network Graphics)
PNG is suitable for images that require transparent backgrounds or high quality without losing any details. Unlike JPEG, PNG uses lossless compression, meaning the image retains its original quality even after compression. Although PNG files are larger than JPEG files, the higher quality and transparency it offers make it very popular for certain applications, so many people change file format to PNG.
GIF (Graphics Interchange Format)
GIF is commonly used for simple graphics and animations. This format supports only 256 colors, which limits its use for complex or high-resolution images. However, its ability to support animation makes it popular for small, looping videos or short animated clips, especially for use in social media and websites.
TIFF (Tagged Image File Format)
TIFF is a high-quality image format that is popular in everyday use. TIFF files can be either lossless compressed or uncompressed, allowing them to retain all image details and quality, making them ideal for archiving and professional image editing. However, due to their large file size, TIFF is not suitable for web use.
SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics)
SVG is a vector-based image format that, unlike raster formats like JPEG and PNG, is not limited by resolution and can be scaled infinitely without losing quality. This makes SVG ideal for logos, illustrations, and any images that need to be resized frequently.
How to change the image file format?
In some cases, if you want to convert TIFF to JPEG format or convert it to a format suitable for printing or web use, you can change the image file format using the following methods.
Using Online Tools
- Go to an online image converter website, such as Convertio, Online-Convert, or Zamzar. Then, upload your image.
- Choose the new file format you want to convert the image to (e.g., from JPEG to PNG or from PNG to SVG).
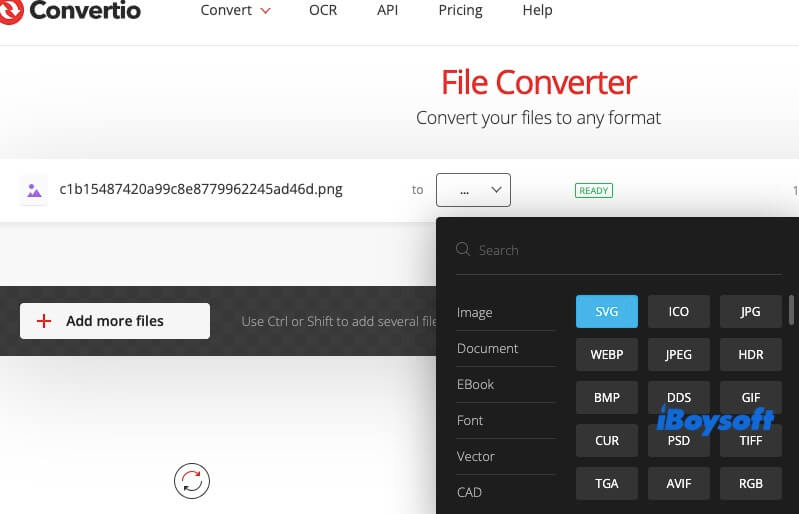
- Click "Convert" and download the new file once the process is complete.
Using macOS Preview (for Mac users)
- Open the image in Preview.
- Go to File > Export.
- Choose the desired format (e.g., PNG, JPEG, TIFF, PDF) from the dropdown menu.
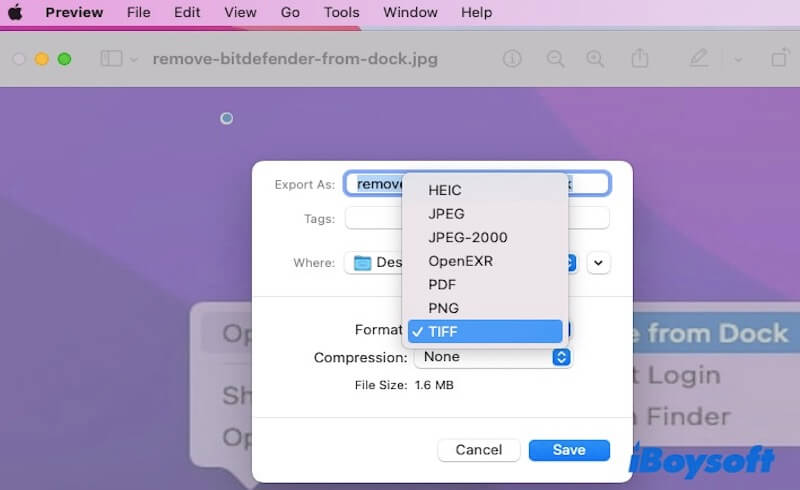
- Click Save to store the image in the new format.
Using Microsoft Paint (for Windows users)
- Open the image in Paint.
- Go to File > Save as and choose the format you want (JPEG, PNG, BMP, etc.).
- Choose the destination folder and save the image.
These methods work for most common image formats and are simple ways to convert an image to a different format for use across different platforms and applications.
Is this article helpful? Please share it.