Although Windows may be altered in many ways through its menus, the most extensive modifications require accessing and altering the registry. While this makes it possible to make all sorts of awesome modifications, it's important to take caution when making registry edits since errors can seriously harm your system. This post will explain what is the Windows Registry, and tell how to backup and restore the Windows Registry on your computer.
What is the Windows Registry?
The Windows Registry is a central database used by the Windows operating system to store configuration settings and options for both the operating system itself and installed applications. It is a critical component for Windows to function properly, as it holds the preferences, settings, and configuration details required for everything from system hardware to software behaviors.
The Registry is organized into a tree-like structure with keys and values. These keys contain information such as:
- User settings - Information about user profiles, preferences, and desktop configurations.
- System settings - Configuration data for operating system components, services, and installed drivers.
- Application settings - Preferences for installed applications, such as how software should behave or where to find certain resources.
The Registry has several root keys, which are the top-level categories where data is stored:
- HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT (HKCR): Contains information related to file associations and COM objects.
- HKEY_CURRENT_USER (HKCU): Stores settings for the currently logged-in user.
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE (HKLM): Contains system-wide settings for hardware and software.
- HKEY_USERS (HKU): Stores settings for all users on the system.
- HKEY_CURRENT_CONFIG (HKCC): Contains information about the current hardware profile used by the machine.
The Registry can be edited using the Registry Editor (Regedit), but this is generally not recommended unless you are certain of what you're doing. Incorrect changes can lead to system instability or even prevent Windows from booting, and backing up the Windows Registry is necessary.
How to back up Windows Registry?
While the Registry is essential, it should be handled with care, and a backup should be made before making any changes to avoid unintended consequences. Just follow the steps below carefully to back up the Windows Registry on your device.
- Press Windows + R to open the Run dialog. Type regedit and press Enter or click OK. If prompted by User Account Control (UAC), click Yes to allow the Registry Editor to open.
- In the Registry Editor, click on File in the top-left corner to back up the entire Registry. Or, you can right-click on the specific key (folder) you want to back up.
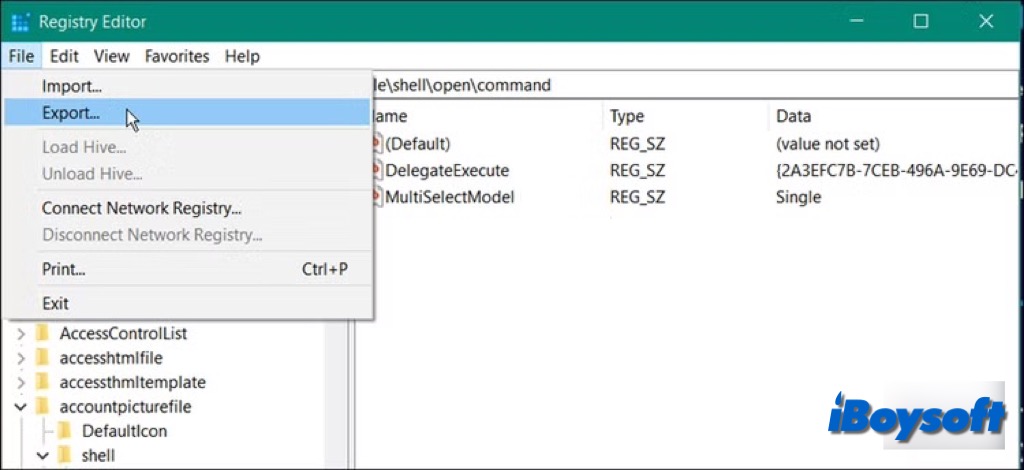
- Select Export from the drop-down menu.
- In the "Export Registry File" window, choose a location to save the backup file.
- In the Export range section, select All to back up the entire registry.
- Give the backup file a name (for example, RegistryBackup.reg), and then click Save. This will create a .reg file that contains the entire Registry, which you can restore later if needed.
How to restore the Windows Registry?
Whether you've accidentally modified the Registry or need to recover it after a system crash, knowing how to restore it can save you from system instability. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to restore the Windows Registry if you have created a backup.
- Find the .reg file you saved during the backup process. It might be on your Desktop or in a designated folder where you saved the backup.
- Double-click the .reg backup file. You'll be prompted with a message asking if you want to merge the file into your Registry.
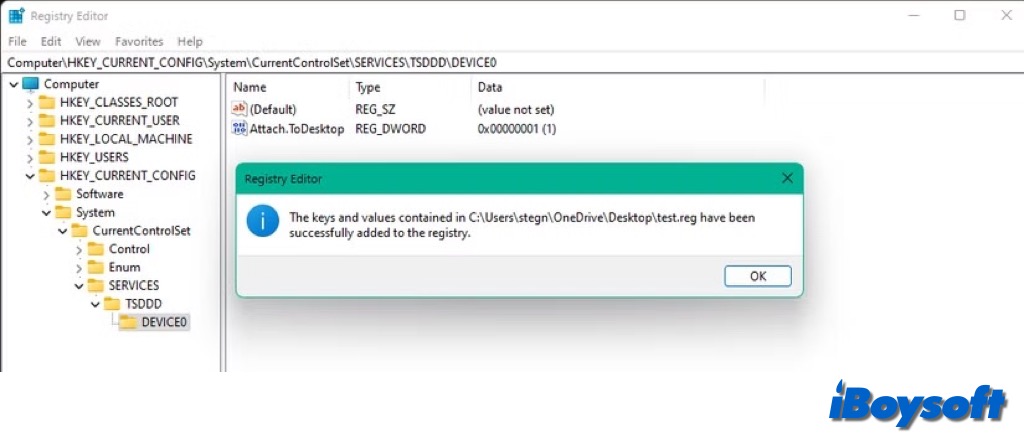
- Click Yes to allow the Registry changes to be applied. A warning message will appear advising you to back up the Registry before making any changes. Since you're restoring, click Yes again to proceed.
- Once the Registry Editor processes the file, you'll see a confirmation that the keys and values have been added to the Registry. Click OK.
- To make sure the restored settings take effect, restart your computer.
Alternatively, you can use System Restore to back up and restore your Windows Registry.
When a system restore point is created, it automatically backs up critical system files, including the Windows Registry. The Registry consists of several hives that contain system and application settings, and they are part of the restore point. When you perform a system restore to a previous point, the system registry, along with other critical system files, is reverted to the state it was in at that restore point.
Help others to learn how to back up and restore the Windows Registry!