When purchasing a USB device, read and write speed need to be considered. A USB device with high-speed performance can significantly improve file transfer efficiency, saving you a lot of time when copying files to your computer and greatly boosting your work productivity.
In this article, we will guide you through the read and write speeds of different types of USBs, how to check USB read and write speed, and how to choose the right USB device for your needs.
How do I check my USB read and write speed on a Mac
By regularly checking your USBs' read and write speed, you can better manage your storage devices. It avoids your Mac's performance degradation or compatibility issues, and improves the convenience and efficiency of your daily use.
Since macOS does not have a built-in feature to test USB read and write speed, it is recommended to use professional third-party software to perform disk speed tests on a Mac.
iBoysoft DiskGeeker for Mac, a professional disk management tool, allows you to test internal drives with two modes and external drives with six modes.
Simply download and launch the software, connect your USB device, click Speed Test, select a test mode, and wait a few seconds to view the USB's read and write speed.
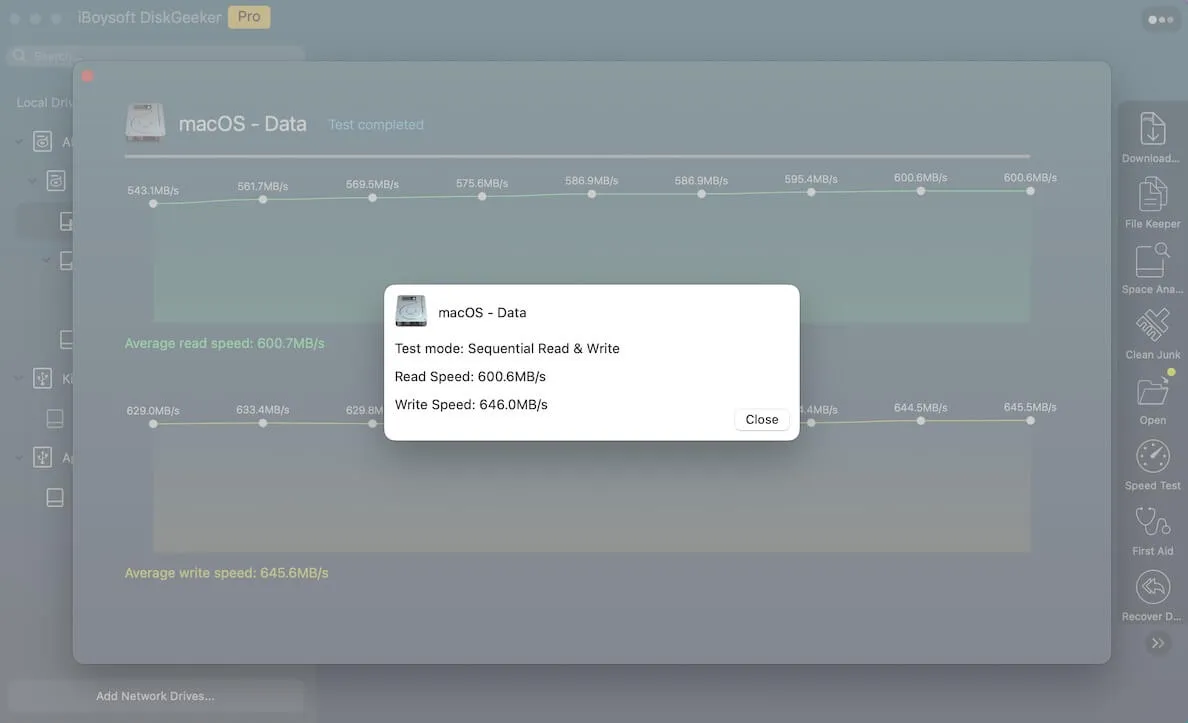
Share this kind of useful tool with your friends if you find it useful!
What is the read-write speed of a USB port
The read and write speed of a USB device can vary depending on the type of USB port it's connected to. Read on to learn about the read and write speeds of different types of USB ports.
- USB 1.0: Introduced in 1996, designed mainly for low-speed peripherals like keyboards and mice. Its data transfer capabilities are very limited by today's standards.
- USB 2.0: A major upgrade, offering much faster speeds for external storage, though still relatively slow for modern large file transfers.
- USB 3.0 and later: Introduced super-speed capabilities, making large file transfers, external SSD usage, and high-definition video work much more practical.
- USB 4: Combines the speed of Thunderbolt 3 and the versatility of USB, ideal for 4K/8K video editing, professional data backup, and gaming peripherals.
| USB Version | Theoretical Max Speed | Average Read Speed | Average Write Speed |
| USB 1.0 | 12 Mbps (1.5 MB/s) | 0.8–1 MB/s | 0.5–0.8 MB/s |
| USB 2.0 | 480 Mbps (60 MB/s) | 20–30 MB/s | 10–20 MB/s |
| USB 3.0 | 5 Gbps (625 MB/s) | 100–150 MB/s | 70–100 MB/s |
| USB 3.1 | 10 Gbps (1250 MB/s) | 400–600 MB/s | 300–500 MB/s |
| USB 3.2 | 20 Gbps (2500 MB/s) | 1000–1600 MB/s | 800–1400 MB/s |
| USB 4 | 40 Gbps (5000 MB/s) | 2000–3500 MB/s | 1500–3000 MB/s |
Should I buy a USB 2.0 or 3.0 flash drive
In general, USB 2.0 drives are more affordable and offer excellent compatibility. However, the read and write speeds are slower than USB 3.0, typically around 25–30MB/s. Therefore, if you occasionally use a USB drive to store a small number of files and don't require transfer speed, a USB 2.0 drive should meet your needs.
USB 3.0 drives offer read and write speeds faster than USB 2.0, usually reaching 100–200MB/s, which can significantly improve work efficiency. It is recommended to choose a USB 3.0 drive if you frequently transfer large files, such as high-definition videos, and want to save time and boost productivity.
It's important to note that USB 3.0 devices are backward compatible with USB 2.0 ports. This means that even if you're using an older device, you can still use a USB 3.0 drive normally. But the transfer speed will be limited by the port's standard.
Share this post about USB read and write speed with more people!
