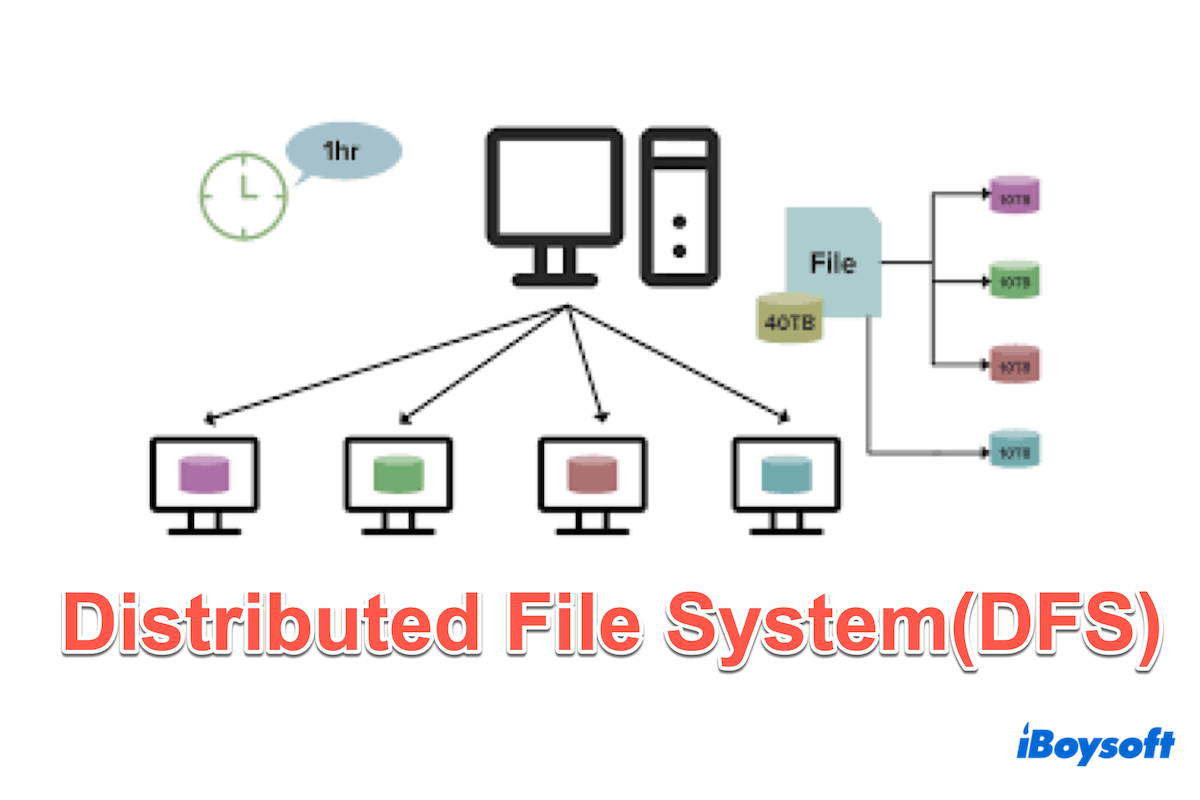
Distributed File System(DFS) is a network file system where files and folders are stored across multiple servers and made available to clients as if they were stored on a single disk.
A network of workstations and mainframes linked via a Local Area Network(LAN) constitutes a setup for a DFS. DFS Distributed File System provides a seamless way to access and manage files across a network, enhancing data availability and scalability.
Then we will explore how the Distributed File System works, its benefits and features, and the main usages.
How does Distributed File System work?
What is a Distributed File System? There are two parts to a Distributed File System: Location Transparency and Redundancy. They will work together to improve data availability by allowing the sharing of data coming from different places.
Distributed File System(DFS) works by spreading files across multiple servers in a network. Simply speaking, when a user accesses a file, DFS automatically determines which server holds that file and retrieves it for the user. This setup improves data availability and scalability and ensures that users can access files efficiently, even if one server goes down.
If you like this post, share it on your social platforms.
Examples and benefits of Distributed File System
Let's move to the applications and benefits of DFS.
Examples of Distributed File System
Several implementations of DFS exist, including many fields:
Microsoft Distributed File System(DFS): It is integrated into Windows Server operating systems, allowing organizations to create a distributed file system using Windows servers.
Google File System(GFS): Developed by Google to handle large-scale distributed data-intensive applications, GFS is used internally by Google for various storage needs.
Network File System(NFS): Commonly used in Unix and Linux environments, NFS allows clients to assess data stored on remote servers, improving seamless file sharing and collaboration.
Apache Hadoop Distributed File System(HDFS): Part of the Apache Hadoop project, HDFS is a distributed file system designed to store and manage large datasets and is commonly used for big data processing and analytics.
Benefits of Distributed File System
Load balancing: DFS enables load balancing by distributing file access requests across multiple servers, which helps environments with high file access demands.
Centralized management: DFS provides centralized management of file resources, allowing users to easily organize and manage files across distributed servers from a single interface.
Scalability: DFS allows for easy scalability by distributing file storage across multiple servers. As the storage needs grow, additional servers can be added to the network without disrupting existing services.
Differences between DFS & NAS & SMB
Network Attached Storage(NAS), Distributed File System(DFS), and Server Massage Block(SMB) are all technologies used for file sharing and storage in networked environments, but they serve different purposes and operate at different levels of the IT infrastructure. Here are the key differences between NAS, DFS, and SMB:

| Purpose | Architecture | Administration | |
| NAS | Store and share files across the network | Dedicated hardware with file system, operating system, and network interface | The management interfaces |
| DFS | Access resources across multiple servers and locations | A logic hierarchy or namespace | Integrated into Windows |
| SMB | Request files from servers over the network | The application layer of the OSI model | Administrative tools provided by the operating system |
In summary, NAS provides dedicated storage appliances for centralized file storage, DFS organizes distributed file resources into a unified namespace, and SMB facilitates file sharing and access between clients and servers over the network.
Moreover, NAS often relies on the SMB protocol for file sharing, whereas DFS can utilize various protocols, including SMB, NFS, and HTTP.
While they serve different purposes, they can complement each other to provide robust file-sharing and storage solutions in networked environments. Share it to help more ones.
Final words
Every coin has two sides, and so does the Distributed File System. By leveraging distributed storage and replication techniques, DFS provides a unified view of files and folders while mitigating the risks associated with single points of failure. But compared to NAS and SMB, it also has some weaknesses. Hope you can have a better judgment while choosing a suitable one.
- QIs NTFS a Distribute File System?
-
A
No, NTFS is not a DFS. It is a proprietary file system developed by Microsoft, primarily used for local storage on individual computers or servers. NTFS is not designed to distribute files across multiple servers in a network like a DFS would.
- QWhat is the difference between a local file system and a distributed file system?
-
A
In a traditional local file system, both users and storage are usually located on the same machine. In contrast, DFS operates in an environment where data can be distributed across numerous hosts on a network, with users accessing the system from various locations.